Solves a system of linear equations with a Cholesky-factored symmetric (Hermitian) positive-definite matrix.
Syntax
FORTRAN 77:
call spotrs( uplo, n, nrhs, a, lda, b, ldb, info )
call dpotrs( uplo, n, nrhs, a, lda, b, ldb, info )
call cpotrs( uplo, n, nrhs, a, lda, b, ldb, info )
call zpotrs( uplo, n, nrhs, a, lda, b, ldb, info )
Fortran 95:
call potrs( a, b [,uplo] [, info] )
C:
lapack_int LAPACKE_<?>potrs( int matrix_order, char uplo, lapack_int n, lapack_int nrhs, const <datatype>* a, lapack_int lda, <datatype>* b, lapack_int ldb );
Include Files
The FORTRAN 77 interfaces are specified in the mkl_lapack.fi and mkl_lapack.h include files, the Fortran 95 interfaces are specified in the lapack.f90 include file, and the C interfaces are specified in the mkl_lapacke.h include file.
Description
The routine solves for X the system of linear equations A*X = B with a symmetric positive-definite or, for complex data, Hermitian positive-definite matrix A, given the Cholesky factorization of A:
| A = UT*U for real data, A = UH*U for complex data | if uplo='U' |
| A = L*LT for real data, A = L*LH for complex data | if uplo='L' |
where L is a lower triangular matrix and U is upper triangular. The system is solved with multiple right-hand sides stored in the columns of the matrix B.
Before calling this routine, you must call ?potrf to compute the Cholesky factorization of A.
Input Parameters
The data types are given for the Fortran interface. A <datatype> placeholder, if present, is used for the C interface data types in the C interface section above. See C Interface Conventions for the C interface principal conventions and type definitions.
uplo |
CHARACTER*1. Must be 'U' or 'L'. Indicates how the input matrix A has been factored: If uplo = 'U', the upper triangle of A is stored. If uplo = 'L', the lower triangle of A is stored. |
n |
INTEGER. The order of matrix A; n ≥ 0. |
nrhs |
INTEGER. The number of right-hand sides (nrhs ≥ 0). |
a, b |
REAL for spotrs DOUBLE PRECISION for dpotrs COMPLEX for cpotrs DOUBLE COMPLEX for zpotrs. Arrays: a(lda,*), b(ldb,*). The array a contains the factor U or L (see uplo). The array b contains the matrix B whose columns are the right-hand sides for the systems of equations. The second dimension of a must be at least max(1,n), the second dimension of b at least max(1,nrhs). |
lda |
INTEGER. The leading dimension of a; lda ≥ max(1, n). |
ldb |
INTEGER. The leading dimension of b; ldb ≥ max(1, n). |
Output Parameters
b |
Overwritten by the solution matrix X. |
info |
INTEGER. If info = 0, the execution is successful. If info = -i, the i-th parameter had an illegal value. |
Fortran 95 Interface Notes
Routines in Fortran 95 interface have fewer arguments in the calling sequence than their FORTRAN 77 counterparts. For general conventions applied to skip redundant or reconstructible arguments, see Fortran 95 Interface Conventions.
Specific details for the routine potrs interface are as follows:
a |
Holds the matrix A of size (n, n). |
b |
Holds the matrix B of size (n, nrhs). |
uplo |
Must be 'U' or 'L'. The default value is 'U'. |
Application Notes
If uplo = 'U', the computed solution for each right-hand side b is the exact solution of a perturbed system of equations (A + E)x = b, where
|E| ≤ c(n)ε |UH||U|
c(n) is a modest linear function of n, and ε is the machine precision.
A similar estimate holds for uplo = 'L'. If x0 is the true solution, the computed solution x satisfies this error bound:
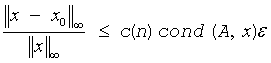
where cond(A,x)= || |A-1||A| |x| ||∞ / ||x||∞ ≤ ||A-1||∞ ||A||∞ = κ∞(A).
Note that cond(A,x) can be much smaller than κ∞ (A). The approximate number of floating-point operations for one right-hand side vector b is 2n2 for real flavors and 8n2 for complex flavors.
To estimate the condition number κ∞(A), call ?pocon.
To refine the solution and estimate the error, call ?porfs.