Reduces a general matrix to upper Hessenberg form by an orthogonal/unitary similarity transformation (unblocked algorithm).
Syntax
call psgehd2(n, ilo, ihi, a, ia, ja, desca, tau, work, lwork, info)
call pdgehd2(n, ilo, ihi, a, ia, ja, desca, tau, work, lwork, info)
call pcgehd2(n, ilo, ihi, a, ia, ja, desca, tau, work, lwork, info)
call pzgehd2(n, ilo, ihi, a, ia, ja, desca, tau, work, lwork, info)
Description
The p?gehd2 routine reduces a real/complex general distributed matrix sub(A) to upper Hessenberg form H by an orthogonal/unitary similarity transformation: Q'*sub(A)*Q = H, where sub(A) = A(ia+n-1 :ia+n-1, ja+n-1 :ja+n-1).
Input Parameters
- n
(global) INTEGER. The order of the distributed submatrix A. (n≥ 0).
- ilo, ihi
(global) INTEGER. It is assumed that sub(A) is already upper triangular in rows ia:ia+ilo-2 and ia+ihi:ia+n-1 and columns ja:ja+jlo-2 and ja+jhi:ja+n-1. See Application Notes for further information.
If n≥ 0, 1 ≤ ilo ≤ ihi ≤ n; otherwise set ilo = 1, ihi = n.
- a
(local).
REAL for psgehd2
DOUBLE PRECISION for pdgehd2
COMPLEX for pcgehd2
COMPLEX*16 for pzgehd2.
Pointer into the local memory to an array of DIMENSION(lld_a, LOCc(ja+n-1)).
On entry, this array contains the local pieces of the n-by-n general distributed matrix sub(A) to be reduced.
- ia, ja
(global) INTEGER. The row and column indices in the global array A indicating the first row and the first column of the submatrix A, respectively.
- desca
(global and local) INTEGER array, DIMENSION (dlen_). The array descriptor for the distributed matrix A.
- work
(local).
REAL for psgehd2
DOUBLE PRECISION for pdgehd2
COMPLEX for pcgehd2
COMPLEX*16 for pzgehd2.
This is a workspace array of DIMENSION (lwork).
- lwork
(local or global). INTEGER.
The dimension of the array work.
lwork is local input and must be at least lwork≥nb + max( npa0, nb ), where nb = mb_a = nb_a, iroffa = mod( ia-1, nb ), iarow = indxg2p ( ia, nb, myrow, rsrc_a, nprow ),npa0 = numroc(ihi+iroffa, nb, myrow, iarow, nprow ).
indxg2p and numroc are ScaLAPACK tool functions;myrow, mycol, nprow, and npcol can be determined by calling the subroutine blacs_gridinfo.
If lwork = -1, then lwork is global input and a workspace query is assumed; the routine only calculates the minimum and optimal size for all work arrays. Each of these values is returned in the first entry of the corresponding work array, and no error message is issued by pxerbla.
Output Parameters
- a
(local). On exit, the upper triangle and the first subdiagonal of sub(A) are overwritten with the upper Hessenberg matrix H, and the elements below the first subdiagonal, with the array tau, represent the orthogonal/unitary matrix Q as a product of elementary reflectors. (see Application Notes below).
- tau
(local).
REAL for psgehd2
DOUBLE PRECISION for pdgehd2
COMPLEX for pcgehd2
COMPLEX*16 for pzgehd2.
Array, DIMENSION LOCc(ja+n-2) The scalar factors of the elementary reflectors (see Application Notes below). Elements ja:ja+ilo-2 and ja+ihi:ja+n-2 of tau are set to zero. tau is tied to the distributed matrix A.
- work
On exit, work(1) returns the minimal and optimal lwork.
- info
(local).INTEGER.
If info = 0, the execution is successful.
if info < 0: If the i-th argument is an array and the j-entry had an illegal value, then info = - (i*100+j), if the i-th argument is a scalar and had an illegal value, then info = -i.
Application Notes
The matrix Q is represented as a product of (ihi-ilo) elementary reflectors Q = H(ilo)*H(ilo+1)*...*H(ihi-1).
Each H(i) has the form H(i) = I - tau*v*v',
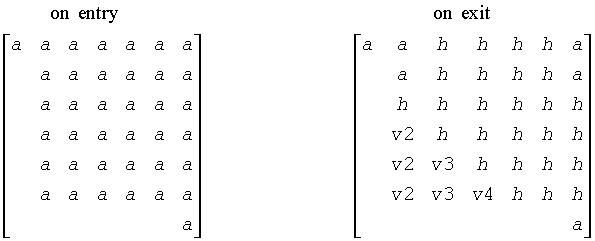
where tau is a real/complex scalar, and v is a real/complex vector with v(1: i)=0, v(i+1)=1 and v(ihi+1:n)=0; v(i+2:ihi) is stored on exit in A(ia+ilo+i:ia+ihi-1, ia+ilo+i-2), and tau in tau(ja+ilo+i-2).
The contents of A(ia:ia+n-1, ja:ja+n-1) are illustrated by the following example, with n = 7, ilo = 2 and ihi = 6:
where a denotes an element of the original matrix sub(A), h denotes a modified element of the upper Hessenberg matrix H, and vi denotes an element of the vector defining H(ja+ilo+i-2).