The general form of the discrete Fourier transform is 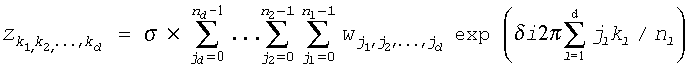
where w is the input sequence, z is the output sequence, both indexed by kl = 0, ... nl-1, for l = 1, ..., d, scale factor σ is an arbitrary real number with the default value of 1.0, and the sign in the exponent is δ = -1 for the forward transform and δ = +1 for the backward transform.
The implementation of FFT supports
forward transforms on input sequences of two domains, as specified
by configuration parameter DFTI_FORWARD_DOMAIN: general
complex-valued sequences (DFTI_COMPLEX domain) and general
real-valued sequences (DFTI_REAL domain). The forward transform maps
the forward domain to the corresponding backward domain, as shown
in Table "Correspondence of Forward and Backward Domain", where the conjugate-even domain
covers complex-valued sequences with the symmetry
property:![]()
Here the overline denotes the complex conjugate, and it is assumed that![]()
Due to this property of conjugate-even sequences, only a part of such sequence is stored in the computer memory, as described in DFTI_CONJUGATE_EVEN_STORAGE.
Forward Domain |
Implied Backward Domain |
|---|---|
Complex (DFTI_COMPLEX) |
Complex (DFTI_COMPLEX) |
Real (DFTI_REAL) |
Conjugate-even |
DFTI_FORWARD_DOMAIN is one of the four settable configuration parameters that do not have a default value. Set them explicitly by calling the DftiCreateDescriptor function.